|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
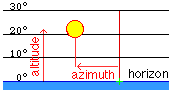 |
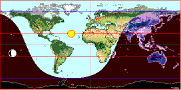
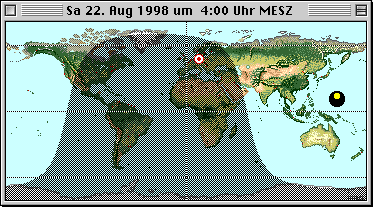
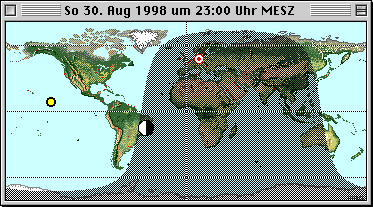
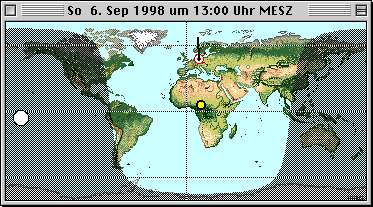
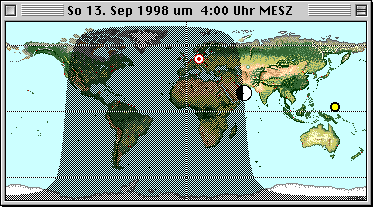
The positions of the Sun and Moon are displayed on
the horizon in equirectangular projection. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The elongation of the Moon from the Sun is the angular distance of the two bodies as viewed from the selected location on the Earth. |
|
The current value can be found in the Java Console: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
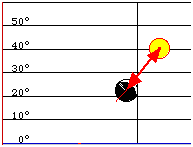
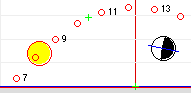
Click the horizon picture to get displayed the altitude, azimuth and time (for the Sun at this azimuth angle). |
 |
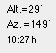 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
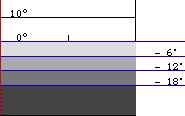
Before sunrise and after sunset the sky is partially illuminated by scattered sunlight (sun below the horizon, elevation < 0).
The times of sunrise, sunset and twilight (civil, nautical and astronomical) are displayed on a clock.
Twilight duration at 50° latitude (minutes before rise):
Twilight duration at 0° latitude (minutes before rise):
Twilight duration at 30° latitude (minutes before rise):
Twilight duration at 60° latitude (minutes before rise): |
|
civil twilight: nautical twilight: astronomical twilight: Lighting-Up Time, Sunrise/Sunset and Twilights (Royal Greenwich Observatory) "Rise, Set, and Twilight Definitions" (U.S. Naval Observatory) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
A new window with a large clock can be opened showing the times of sunrise, sunset and twilight. |
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
The times of rise, transit (meridian passage), and
setting for Sun and Moon are local times. They should
coincide within 1 or 2 minutes with the values
computed by more complex algorithms. The results are
written to the Java Console. |
Details: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
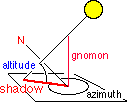
Altitude (Elevation) and Azimuth of Sun and Moon
|
|
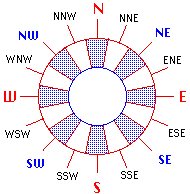
the altitude (elevation) is the angular distance measured above the horizon, the azimuth is the
angular distance measured along the horizon, 0 deg. = N, 90 deg. = E
|
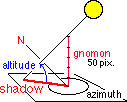
 In nautics, the azimuth is measured eastwards from the North point, in astronomy westwards from the South point. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Azimuth |
The azimuth angle at rise and set (Azo) depends on the current declination (delta) and on the latitude (beta) of the observer: |
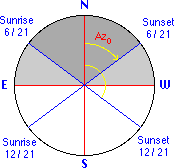 |
For summer solstice (delta = +23.5°) and beta=45° N: and for winter solstice (delta = -23.5°): |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
The symbols are the sub-solar and sub-lunar points (Geographical Position) of Sun and Moon, where the line from the Sun or Moon to the centre of the Earth intersects its surface. The coordinates of the Geographical Position (latitude and longitude) are the same as the declination and Greenwich hour angle (GHA). The illuminated part of the moon is displayed as it is seen from the Sun. The Tropic of Cancer
(parallel of latitude 23.5° north of the equator)
is the northernmost place in the world where the sun
is ever directly overhead. |
An observer positioned in the Geographical Position (GP) will see the Sun or Moon directly in the vertical, above his head. 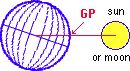 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
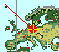 |
displays the red shadow of a 50 pixel vertical stick (gnomon) on the horizontal plane at the new location. Shadows are cut off if exceeding the right or upper border of the map.
|
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
and the geographical coordinates of the clicked location (latitude N/S, longitude E/W).
|
..
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
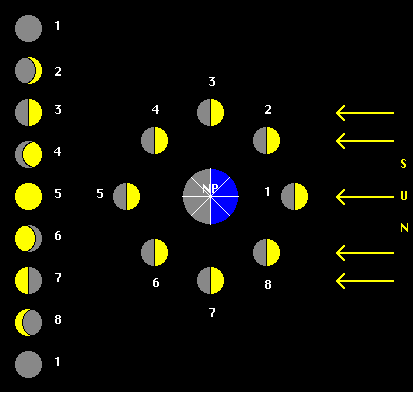
Age of the Moon, phase, illumination
|
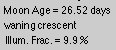 The time taken by the Moon on its orbit, from New Moon to next New Moon, is 29.53 days. The illuminated fraction is the ratio of the apparent illuminated area of the disk to the total area of the disk, as seen from the Earth.
|
|
The phases of the Moon and the illuminated fraction are (practically) independent of the observer's location on the Earth. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
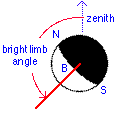 |
the terminator NBS (an ellipse) is the line separating the dark and the illuminated part of the Moon. |
The angle of the Moon's bright limb to the local zenith is listed in the Java console. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
For the current month, date and time (UT) of the previous or next New Moon are computed. |
. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Distance of the Moon |
|
The distance of the Moon from Earth varies between 356410 km (perigee) and 406740 km (apogee). |
. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
user input /
|
|
for a new location: |
- degrees latitude as |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
enter longitude, and
press return key |
- degrees longitude as
a |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
You may also enter a new location by clicking the word map, |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
The coordinates of the user location are stored (during applet's lifetime) and can be recalled by the location menu item "User Input". |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Open "Sme.html" in Netscape's Composer or in any HTML or text editor. Enter the parameter values of "location", "latitude" and "longitude" parameters:
|
<APPLET
CODE="SunMoonEarthxxx.class" <PARAM name="email" value="replace"> </APPLET> |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Look up your coordinates: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
time difference between local zone time and Greenwich
Time (GMT),
+ 1 h is the value computed from the longitude value, without respect to the DST and which may differ from the actual time zone offset. The GMT date may be different from the local date: |
Central European Daylight Time = GMT + 2 hours |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
The declination and Greenwich hour angle (GHA) are the coordinates (latitude and longitude) of the Geographical Position (GP) of Sun or Moon, where the line from the Sun or Moon to the centre of the Earth intersects its surface. 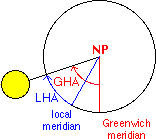 The local hour angle is: |

|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
The Equation of Time
is the difference between the time determined by a
sundial and the clock time. It is due to the obliquity
of the Earth's axis and the unequal motion of the
Earth (ellipse). The value, computed for 12:00 UT, is
between -14 :20 min (near Feb 12) and +16:24 min (near
Nov 4). |
For detailed information: Sundials on the Internet: Equation of Time -- Problem in
Astronomy
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
To write the data to the browser's "Java Console" / "Java Messages" window, check the box and press the "now" button or select date and time. The Java window can be opened from the browser's main menu, and then be printed. Netscape 4.5: Set options "Web Browser" "Java" before. |
Example of data output. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Instead of using the menus for hour, date and month, ... |
You may use the keys
"m", "d", "h", "n" to increase the
month, date, hour, or minute |
. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
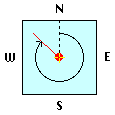
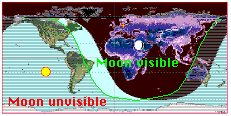
Check the "Moon" box to see the diurnal path of the
moon (green), |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Eclipses of the Sun and the Moon
|
An Eclipse of the sun may occur at New Moon, an eclipse of the Moon at New Moon, Check the moon phases |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parallactic Angle of
the Sun |
The parallactic angle of
the Sun is the angle "at the Sun".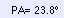 |
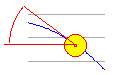 |
The parallactic angle on the prime vertical is equal to 90°-latitude. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||